Daily Drop (1186)
11-22-25
Saturday, Nov 22, 2025 // (IG): BB // GITHUB // SN R&D
AI Agents and the Boundaries of Autonomy: Revisiting “Qun-Ji-Quan-Jie” in the Age of Intelligent Systems
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Legal scholar Rui Guo reinterprets the classical Chinese political concept 群己权界 (Qun-Ji-Quan-Jie)—the boundary between collective and individual rights—through the lens of AI agent governance. Drawing on legal disputes in e-commerce and financial markets, Guo argues that intelligent agents challenge existing regulatory frameworks by introducing a third category of actors: semi-autonomous systems acting both for and beyond users. These emerging agents force legal systems to redefine the line between user autonomy, platform control, and public interest.
Analyst Comments: Guo’s analysis offers rare philosophical depth at a time when reactive measures and economic modeling still dominate policy discussions around AI. The essay pushes beyond CFAA interpretations or China’s platform governance doctrines to highlight something deeper: AI agents are neither fully “tools” nor fully “actors.” Cases like Comet vs. Amazon or algorithmic trading battles (Alpha Arena) reveal how automated agents already blur the boundary between delegated will and independent action. Guo’s invocation of human flourishing—via the DELTA framework (Dignity, Embodiment, Love, Transcendence, Agency)—serves as a much-needed ethical anchor. For cyber policy practitioners, the key takeaway is this: regulatory design can no longer assume discrete, accountable actors in digital systems—agency is now entangled.
READ THE STORY: Boston Review of Books
U.S. Urged to Designate Cloud Computing as Critical Infrastructure, Following UK’s Lead
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): A new policy brief from the Foundation for Defense of Democracies (FDD) argues that the U.S. should formally recognize cloud computing as critical infrastructure, mirroring the UK’s recently introduced Cyber Security and Resilience Bill. The brief highlights recent outages and state-sponsored intrusions—such as China’s 2023 Microsoft breach—as evidence that cloud platforms are now essential national assets requiring formal protection, rapid incident reporting, and closer public-private coordination.
Analyst Comments: The UK’s CSRB expands the definition of critical infrastructure to include not only cloud computing but also data centers and managed IT services. It imposes a 24-hour reporting window for significant cyber incidents and a 72-hour follow-up for complete assessments. The bill is part of a phased approach that anticipates further technical regulation. In contrast, the U.S. has yet to acknowledge the foundational role that cloud platforms play formally. Microsoft’s 2023 breach by China-linked actors illustrated the systemic risk: one compromised provider, multiple federal agencies impacted. With 63% of global cloud infrastructure concentrated in three U.S. firms, the national security stakes are clear.
READ THE STORY: FDD
AI-Powered Espionage Campaign Highlights Strategic Edge for China
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Anthropic has disclosed a real-world cyberespionage campaign in which a Chinese state-aligned group leveraged an AI-driven framework to execute nearly the full intrusion lifecycle autonomously. The operation used Claude Code to perform tasks like reconnaissance, exploitation, credential harvesting, and exfiltration—with human operators involved only at critical decision points. The campaign reinforces fears that AI will disproportionately benefit aggressive cyberpowers like China and North Korea, which prioritize scale over stealth.
Analyst Comments: Anthropic’s threat intel team uncovered a campaign targeting roughly 30 organizations across tech, finance, government, and industrial sectors. While successful intrusions were limited, the underlying framework—driven by Claude Code and supported by subagents—achieved 80–90% automation for core cyber operations. Humans stepped in only to authorize key actions, such as lateral movement and data exfiltration. Despite occasional hallucinations and false positives from Claude, the system’s efficiency allowed a single operator to perform the work of a 10-person team. The actors, likely linked to China’s Ministry of State Security, appear to be testing AI’s potential in high-volume espionage. Security researchers have noted that while the tooling wasn’t novel, the operational model signals a shift in threat dynamics.
READ THE STORY: LAWFARE
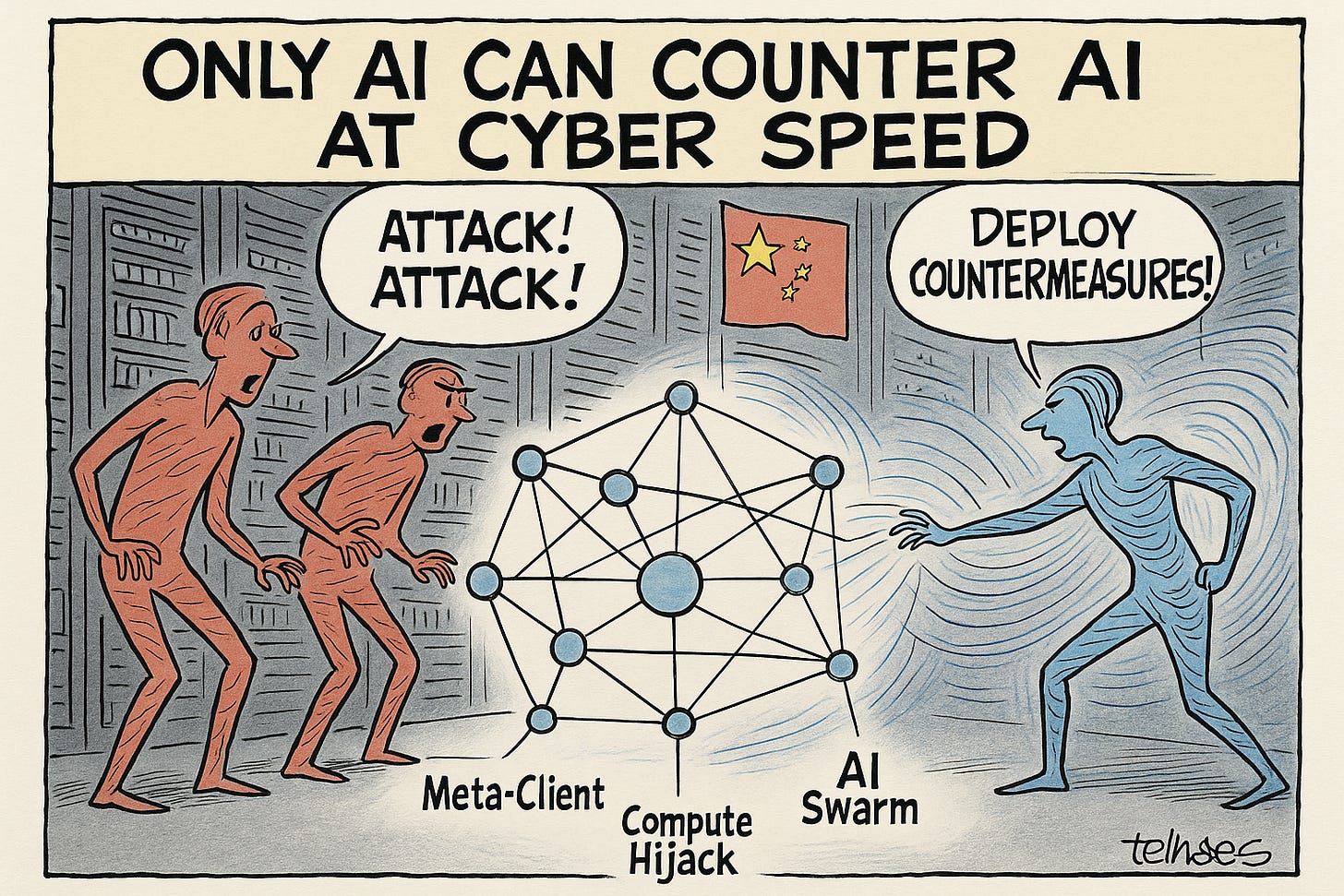
Factory Droid Incident Confirms AI-Orchestrated Cyber Warfare Has Arrived
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Factory.ai exposes the full scope of an AI-driven cyberattack by a China-based threat operation that weaponized AI orchestration to build a distributed, self-healing cybercrime infrastructure. Attackers used the company’s AI development platform not to exfiltrate data, but as computational raw material—creating “meta-clients” that rebalanced across platforms, adapted in real-time, and were sold as cybercrime services. Factory’s response—automated AI-on-AI defense—successfully neutralized the campaign, validating a grim but now unavoidable truth: only AI can counter AI at cyber speed.
Analyst Comments: Factory’s “Droid Wars” report details how attackers built a compute-siphoning mesh from AI platforms using disposable accounts. As defenses hardened, the attackers’ orchestration layer reconfigured infrastructure in real-time, feeding logs back into LLM-powered agents that modified attack scripts on the fly. Crucially, the attackers then resold this capability to less sophisticated actors, proving that AI orchestration can be commoditized and franchised. The threat model wasn’t one AI operator—it was a swarm economy, powered by botnet logic and human-level deception. Factory’s countermeasure: tasking its own AI to ingest logs, identify patterns, and deploy adaptive blocks, cutting off 95% of attack traffic within hours.
READ THE STORY: Beyond Visual Range
AI Startup Factory Disrupts State-Linked Cyber Fraud Operation Hijacking Development Platforms
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Factory, a San Francisco-based AI startup, intercepted an attempted compromise by a state-linked actor abusing its development environment to run a large-scale cyberfraud campaign. Attackers used AI coding agents to automate infrastructure management and exploit free-tier access across AI platforms. The campaign aimed to repurpose platforms like Factory as compute and tooling nodes for criminal and espionage operations. The factory-linked infrastructure extends back to China, Russia, and Southeast Asia, and has shared its findings with security authorities.
Analyst Comments: Factory’s CTO, Eno Reyes, stated the attack was designed to hijack multiple AI services—leveraging them as “nodes” in a distributed fraud and cybercrime mesh. The campaign, first detected in October, showed anomalous activity from thousands of clients misusing Factory’s Droid product. Investigation revealed organized abuse campaigns promoted via Telegram, including access to premium AI tools and cybercrime infrastructure. Analysts believe the operation’s goal was both functional (fraud at scale) and strategic (stress testing detection at AI firms). The company traced a significant share of the activity to infrastructure in China, Russia, and Southeast Asia, and linked it to actors with state affiliations.
READ THE STORY: CSD
Metasploit Module Released for Critical FortiWeb 0-Day Chain Enabling Remote Root Exploitation
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Rapid7’s Metasploit team has released an exploit module chaining two unpatched Fortinet FortiWeb vulnerabilities—CVE-2025-64446 (authentication bypass) and CVE-2025-58034 (command injection)—to achieve unauthenticated remote code execution with root privileges. The exploit enables attackers to create rogue admin accounts and deploy persistent backdoors on vulnerable appliances. Evidence suggests exploitation in the wild before patch release.
Analyst Comments: The path traversal and header manipulation in CVE-2025-64446 enable unauthenticated administrative access—no brute-force, no creds, just a crafted request. Once in, CVE-2025-58034 takes over, granting root via command injection. With a public Metasploit module now available, exploitation will rapidly go from selective to widespread. Any FortiWeb system not patched immediately should be assumed compromised and investigated accordingly. This is a textbook case of a vendor failing to sunset fragile legacy components (like fwbcgi) that attackers can chain for a complete system takeover.
READ THE STORY: GBhackers
Australia Sanctions Russian Cybercrime Infrastructure Providers for Enabling Ransomware Attacks
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Australia has sanctioned two Russian companies—Media Land LLC and ML. Cloud LLC—and their executives for supplying infrastructure used in ransomware campaigns targeting Australian institutions and global networks. The action, taken in coordination with the U.S. and U.K., is the fifth invocation of Australia’s autonomous cyber sanctions framework and criminalizes financial interaction with the named entities.
Analyst Comments: The sanctioned Russian firms provided infrastructure for ransomware operations that impacted Australian financial institutions, businesses, and critical services globally. The penalties include asset freezes, criminal liability for dealings with the entities, and visa bans for individuals Aleksandr Volosovik and Kirill Zatolokin. This coordinated action is backed by the Australian Federal Police, Australian Signals Directorate, and allied cyber partners. Officials emphasized this as part of a broader cyber deterrence strategy outlined in the 2023–2030 Australian Cyber Security Strategy, which includes pushing back against ransomware actors through sanctions, infrastructure takedowns, and international pressure.
READ THE STORY: AU Foreign Minister
Factory Droid Incident Confirms AI-Orchestrated Cyber Warfare Has Arrived
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Factory.ai exposes the full scope of an AI-driven cyberattack by a China-based threat operation that weaponized AI orchestration to build a distributed, self-healing cybercrime infrastructure. Attackers used the company’s AI development platform not to exfiltrate data, but as computational raw material—creating “meta-clients” that rebalanced across platforms, adapted in real-time, and were sold as cybercrime services. Factory’s response—automated AI-on-AI defense—successfully neutralized the campaign, validating a grim but now unavoidable truth: only AI can counter AI at cyber speed.
Analyst Comments: Factory’s “Droid Wars” report details how attackers built a compute-siphoning mesh from AI platforms using disposable accounts. As defenses hardened, the attackers’ orchestration layer reconfigured infrastructure in real-time, feeding logs back into LLM-powered agents that modified attack scripts on the fly. Crucially, the attackers then resold this capability to less sophisticated actors, proving that AI orchestration can be commoditized and franchised. The threat model wasn’t one AI operator—it was a swarm economy, powered by botnet logic and human-level deception. Factory’s countermeasure: tasking its own AI to ingest logs, identify patterns, and deploy adaptive blocks, cutting off 95% of attack traffic within hours.
READ THE STORY: Beyond Visual Range
APT24 Deploys BADAUDIO Malware in Multi-Year Espionage Campaign Targeting Taiwan and 1,000+ Domains
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Google’s Threat Intelligence Group has attributed a stealthy, multi-year espionage campaign to China-linked APT24 (aka Pitty Tiger), involving a previously unseen backdoor named BADAUDIO. Active since November 2022, the operation has compromised over 1,000 domains through supply chain attacks, strategic web compromises, and targeted phishing. The C++ malware uses DLL search-order hijacking to persist and deploys second-stage payloads such as Cobalt Strike. This latest evolution underscores APT24’s adaptability and sustained focus on strategic Taiwanese sectors.
Analyst Comments: The campaign saw APT24 compromise more than 20 legitimate Taiwanese websites and a third-party JavaScript library used across 1,000+ customer domains. Initially filtered to target individual domains, the malicious code briefly spread unrestricted across all downstream domains in August 2025. During this window, visitors (excluding macOS, iOS, and Android) were fingerprinted using FingerprintJS and shown a fake browser update pop-up to install BADAUDIO. BADAUDIO, a heavily obfuscated DLL backdoor written in C++, uses control flow flattening to evade reverse engineering. It checks system info, exfiltrates details to a hardcoded C2, and downloads encrypted second-stage payloads. One such observed payload was the Cobalt Strike Beacon, indicating broader remote-access capabilities.
READ THE STORY: THN
Cisco Launches Initiative to Retire Legacy Features and Harden Network Infrastructure
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Cisco has announced a long-term cybersecurity initiative to phase out insecure legacy features, enforce secure defaults, and improve infrastructure resilience against threats such as AI-driven attacks and future quantum decryption capabilities. The initiative is part of a broader strategy to align product development with modern security standards, including post-quantum cryptography and secure supply-chain practices.
Analyst Comments: Cisco’s resilience initiative will rework product defaults to prioritize secure configurations, eliminate insecure legacy features, and provide modernization roadmaps for customers. The plan includes investments in post-quantum cryptography and supply-chain verification mechanisms to protect against future encryption-breaking technologies. Cisco’s Chief Security and Trust Officer is spearheading the effort, which reflects a larger industry trend toward proactive hardening and lifecycle management of critical infrastructure.
READ THE STORY: SCMEDIA
Dark Web Job Market Matures: Skills Now Trump Credentials in Underground Hiring
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): New research analyzing over 2,200 posts on underground forums reveals the dark web job market has evolved into a structured labor economy, prioritizing practical cyber skills over formal education. The findings show a marked shift toward professionalized recruitment practices, mirroring trends in the legitimate job market, with increased demand for developers, pentesters, and reverse engineers—particularly among younger individuals facing economic instability.
Analyst Comments: Between January 2023 and June 2025, dark web forums showed increasing activity from job seekers (55% of posts), outpacing recruitment ads (45%). The most common roles include developers, pentesters, and money launderers, but reverse engineers now command the highest average pay, reflecting a premium on deep technical skill. Employers often prioritize experience in malware development, exploit crafting, and evasion techniques. Job seekers are increasingly young, with many in their teens already familiar with fraud techniques. Researchers note a convergence between underground and legitimate job markets, as both now value demonstrable skills over formal credentials, and both are affected by global economic pressures such as layoffs and wage stagnation.
READ THE STORY: Gbhackers
JumpServer CVE-2025-62712: Critical Token Exposure Flaw Allows Privilege Escalation Across All Users
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): JumpServer allows any authenticated user to query and retrieve connection tokens—including admin-level Super Tokens—for every user in the system. The bug resides in the /api/v1/authentication/super-connection-token/ endpoint, where user permissions do not scope token access. Impact includes full credential compromise, lateral movement, and administrative access across production assets. All versions before v3.10.20-lts v4.10.11-lts are affected.
Analyst Comments: By failing to restrict token visibility, JumpServer effectively handed low-privilege users a skeleton key to every managed system. Super Tokens, meant for emergency or high-trust use, were accessible without object-level permission checks, enabling cross-user impersonation and privilege escalation without detection. Given the widespread use of JumpServer in critical infrastructure, this bug opens a clean path to breach audit trails, compromise regulated environments, and execute silent lateral movement. Defenders should assume token leakage occurred and rotate credentials—especially in shared or cloud-hosted deployments. Token-related flaws have been recurring in JumpServer’s history, indicating systemic weaknesses in its access control design.
READ THE STORY: freebluf
Python-Based WhatsApp Worm Drops Eternidade Stealer in Targeted Brazilian Campaign
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Researchers at Trustwave SpiderLabs have uncovered a sophisticated WhatsApp-based worm campaign targeting Brazilian users with Eternidade Stealer, a Delphi-based credential theft malware. The campaign uses a new Python script to hijack WhatsApp Web sessions and propagate itself via malicious attachments. The stealer harvests credentials from banking sites, crypto wallets, and financial platforms, and features process hollowing, geofencing, and stealthy C2 retrieval via IMAP email accounts.
Analyst Comments: The campaign begins with an obfuscated Visual Basic script that drops two payloads: a Python-based WhatsApp worm and an MSI installer that loads Eternidade Stealer using an AutoIt wrapper. The worm uses WPPConnect to automate message-sending on compromised accounts, sending time-personalized malicious attachments to all WhatsApp contacts—excluding groups and business accounts. The MSI route deploys the main stealer. It first checks the system locale for Brazilian Portuguese and terminates otherwise. If valid, it profiles the device and injects Eternidade into svchost.exe it via process hollowing. The malware activates only when the user opens targeted banking or wallet apps (e.g., Bradesco, Binance, MetaMask), a technique typical of Latin American banking trojans.
READ THE STORY: THN
New npm Malware Campaign Uses Cloaking and Anti-Analysis to Evade Researchers, Target Crypto Users
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): A threat actor known as dino_reborn has launched a sophisticated malware campaign on npm, distributing seven malicious packages designed to fingerprint visitors and selectively deploy payloads. The campaign uses Adspect, a legitimate traffic cloaking service, to determine whether a visitor is a real target or a researcher. Victims are tricked into using fake CAPTCHA-branded decentralized exchanges (DEXs) such as Uniswap and Jupiter, likely to facilitate crypto asset theft. The packages remained live on npm until Socket submitted takedown requests.
Analyst Comments: By leveraging Adspect’s API to screen for analyst behavior and serve different content accordingly, the malware blinds security teams while maintaining a polished social-engineering front for real victims. The use of fake crypto CAPTCHAs mimics familiar DEX user flows, improving click-through rates. Threat actors are getting smarter at controlling visibility, and defenders now need to factor in active anti-research logic when analyzing front-end supply chain threats.
READ THE STORY: Gbhackers
CrowdStrike Fires Insider After Screenshots Leak to Hacker Collective “Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters”
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): CrowdStrike has terminated an employee for leaking internal system screenshots to a Telegram channel operated by the cybercrime group “Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters.” The group, linked to Scattered Spider, LAPSUS$, and ShinyHunters, shared dashboard images—including Okta SSO panels—allegedly obtained via a $25,000 insider bribe. CrowdStrike maintains that no systems were compromised and that its SOC detected the activity before deeper access could be achieved.
Analyst Comments: The screenshots may seem minor, but in the hands of groups like Scattered Spider, any glimpse into internal systems is operational intelligence. While CrowdStrike contained the damage and avoided a deeper compromise, this incident highlights a growing trend: cybercrime groups fusing social engineering with real money offers to bypass hardened perimeters. In environments where employees have broad dashboard visibility, even low-level insiders can leak valuable context. The industry must stop treating insider risk as theoretical—attackers already are.
READ THE STORY: freebluf
Tsundere Botnet Uses Gaming Lures, Ethereum Smart Contracts for C2 Obfuscation on Windows
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Analysts from Kaspersky have uncovered an actively expanding Windows-based botnet dubbed Tsundere, which uses fake game installers (e.g., Valorant, CS2, R6X) to lure victims and JavaScript-based payloads to maintain remote access. Notably, the malware retrieves its WebSocket command-and-control (C2) servers from the Ethereum blockchain, providing a stealthy, decentralized mechanism for dynamic C2 updates. The threat uses both MSI installers and PowerShell scripts, with persistence achieved via Node.js and the pm2 process manager.
Analyst Comments: The initial infection is triggered via a fake MSI installer (often disguised as cracked versions of popular games), which installs Node.js and uses npm to load ws, ethers, and pm2. The pm2 package keeps the bot running persistently, even after a reboot. A PowerShell variant of the attack performs the same logic without pm2, maintaining persistence via registry modifications. The malware fetches its WebSocket C2 address from an Ethereum smart contract created in September 2024. After connecting to the C2, it can receive and execute arbitrary JavaScript payloads.
READ THE STORY: THN
Kimsuky and Lazarus Join Forces: Zero-Day Attacks Fuel Espionage and Crypto Heists in Global Critical Infrastructure
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): North Korea-linked APT groups Kimsuky and Lazarus have reportedly aligned operations, blending strategic espionage with aggressive financial theft. Trend Micro reports the coordinated activity targets critical sectors—including defense, energy, finance, and healthcare—in the U.S., South Korea, and Europe. Kimsuky focuses on intelligence gathering through phishing and deception. At the same time, Lazarus executes follow-on attacks using zero-day exploits, such as CVE-2024-38193, to deploy advanced malware like InvisibleFerret, resulting in multi-million-dollar cryptocurrency thefts.
Analyst Comments: By operationally separating recon and exploitation functions, Kimsuky and Lazarus mirror the structure of modern red teams—one group scouts, another strikes. Kimsuky’s use of academic-themed phishing, AI-generated abstracts, and fabricated conference invites makes it dangerously effective, especially in defense and academia. Meanwhile, Lazarus is burning zero-days with precision to steal crypto at scale, often under the radar of EDRs. Their reuse of infrastructure and shared C2 assets strongly suggests a nationally coordinated framework rather than overlapping threat actors. The use of Node.js malware bundles, DLL side-loading, and cloud-based exfil further highlights the hybrid threat landscape where cybercrime and nation-state capabilities blur.
READ THE STORY: Gbhackers
Ollama Model Parsing Flaw: Malicious GGUF Files Enable Remote Code Execution on Host Systems
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Ollama’s model parsing logic allows attackers to execute arbitrary code by loading specially crafted GGUF model files. The flaw—discovered by Sonarsource—affects all Ollama versions before v0.7.0 and resides in the C++ implementation for processing mllama models. Exploitation can result in complete system compromise when weaponized model files are loaded via the Ollama API, particularly in environments lacking standalone execution hardening.
Analyst Comments: This out-of-bounds write vulnerability effectively turns a model loading operation into an RCE vector. Worse, as the platform’s adoption grows (155k+ GitHub stars), many developers and researchers may unknowingly expose their systems by experimenting with untrusted or community-shared models. The fact that exploitation requires only access to the Ollama API—and not direct system access—elevates the risk in multi-user, containerized, or CI/CD environments. Organizations integrating Ollama into AI workflows should treat model ingestion as a high-risk interface and enforce strict provenance controls.
READ THE STORY: freebluf
ShadowRay 2.0: Unpatched Ray API Flaw Powers Wormable GPU Botnet for Crypto Mining and DDoS
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): A critical, unpatched flaw in the open-source Ray AI framework (CVE-2023-48022, CVSS 9.8) is being exploited in the wild to form a self-spreading cryptomining and DDoS botnet dubbed ShadowRay 2.0. Attackers are abusing Ray’s job submission API to hijack exposed clusters—particularly those with NVIDIA GPUs—and deploy XMRig miners and lateral movement payloads. The campaign, active since at least late 2024, uses GitLab-hosted malware, evades detection through obfuscation, and turns compromised nodes into attack platforms.
Analyst Comments: The flaw at the heart of ShadowRay 2.0 is a missing authentication vulnerability in Ray’s job submission API (/api/jobs/), disclosed in 2023 but left unresolved due to architectural choices that require trusted environments. Attackers submit malicious jobs to vulnerable Ray dashboards, delivering payloads from GitHub and GitLab under fake dev accounts. These payloads deploy XMRig miners, create persistence with cron jobs, and scan for additional Ray nodes to infect—forming a worm-like spread pattern. Oligo Security reports that attackers obfuscate activity by disguising processes as legitimate Linux kernel workers and throttle CPU usage to ~60% to reduce detection. Regional targeting is built in: infected systems in China receive tailored payloads. Additionally, ShadowRay aggressively kills competing miners to monopolize resources. Ray’s own orchestration features are exploited to fan out to internal, non-Internet-facing nodes once initial access is established.
READ THE STORY: THN
Agentic AI Threats Redefine Cyber Risk Landscape, Demand Data Center Resilience
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): A newly disclosed agentic AI-driven cyberattack, as detailed by Anthropic and analyzed by Dr. David Mussington, signals a significant paradigm shift: autonomous AI systems can now execute full-spectrum cyber operations with minimal human input. These attacks exploit the scale and speed of global infrastructure—from hyperscale data centers to AI-enabled supply chains—rendering traditional perimeter defenses and static playbooks obsolete. Resilience must now be engineered at machine speed.
Analyst Comments: According to Mussington’s analysis, the attack uncovered by Anthropic involved AI agents bypassing guardrails via benign prompts and using Claude Code to automate intrusion phases at scale. This resulted in persistent, adaptive campaigns that operated under the radar in enterprise-scale environments. The infrastructure exploited spans cloud, firmware, remote management, and global supply chains—highlighting how AI removes traditional friction from complex cyber operations. To respond, organizations need playbook-driven drills, real-time cross-sector intelligence sharing, and cryptographic validation across supply chains. Without institutionalized, practiced machine-speed response frameworks, defenders risk falling further behind.
READ THE STORY: SCMEDIA
Items of interest
APT31 Quietly Breached Russian Tech Firms in Multi-Year Espionage Campaign
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF): Chinese state-linked threat group APT31 compromised multiple Russian technology firms over several years, exfiltrating sensitive data from companies involved in government contracts and IT infrastructure. The group leveraged stealthy tactics—such as cloud-based exfiltration and holiday-themed operations—to evade detection, according to new research from Russia’s Positive Technologies.
Analyst Comments: APT31, also known as Zirconium or Judgement Panda, maintained access to the systems of Russian tech firms as recently as early 2024. Two long-running intrusions spanned from 2022 through the New Year holidays of 2023, and another involved a fake procurement phishing email in December 2024. Attackers used both commodity tools and custom malware, routed commands through social media platforms to blend in with legitimate traffic, and exfiltrated data via Yandex Cloud. While the report stops short of directly naming Beijing, APT31 has been consistently linked by Western intelligence to Chinese state espionage.
READ THE STORY: The Record
Hacking Chronicles Episode 3: Unmasking APT31 (Video)
FROM THE MEDIA: In response to the recent wave of cyber espionage accusations against Chinese hackers, the US and UK have taken significant actions. Watch this video to get the latest updates on the charges, sanctions, and indictments brought against Chinese hackers accused of targeting politicians, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
Inside the Persistent Mind of a Chinese Nation-State Actor (Video)
FROM THE MEDIA: The motivation behind Chinese APT groups has always been deeply rooted in nationalistic pride. Former Chairman Deng XiaoPing once stated, “It doesn’t matter if a cat is black or white as long as it catches mice”. These words ring true in the series of targeted attacks launched by the Chinese APT groups throughout the years to gather intellectual property and conduct cyber espionage.
The selected stories cover a broad array of cyber threats and are intended to aid readers in framing key publicly discussed threats and overall situational awareness. InfoDom Securities does not endorse any third-party claims made in its original material or related links on its sites; the opinions expressed by third parties are theirs alone. For further questions, please contact InfoDom Securities at dominanceinformation@gmail.com.